Getting straight to the point. How do we start with creating APIs using gin which is a HTTP web framework written in golang.
Step 1
Get the gin library to golang project. Run the below command in the golang project directory to get the gin package.
go get github.com/gin-gonic/gin@latest
Step 2
Configure gin in the main file. Make sure the main function is written in a file whose package is also main.
Golang standard is to keep the main file in the directory cmd/server.
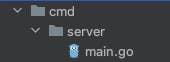
The below code snipped also shows how to gracefully stop/shutdown gin server.
package main
import (
"context"
"log"
"net/http"
"os"
"os/signal"
"syscall"
"time"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
func main() {
port := ":8080"
engine := gin.New()
server := &http.Server{
Addr: port,
Handler: engine,
}
chanErrors := make(chan error)
go func() {
chanErrors <- runServer(server)
}()
chanSignals := make(chan os.Signal, 1)
signal.Notify(chanSignals, os.Interrupt, syscall.SIGTERM)
select {
case err := <-chanErrors:
log.Fatalf("Error while starting server %s", err)
case s := <-chanSignals:
log.Printf("Shutting down server in few seconds due to %s", s)
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), 5*time.Second)
defer cancel()
if err := Close(ctx, server); err != nil {
log.Fatal("Server forced to shutdown: ", err)
}
log.Print("Server exiting gracefully")
}
}
func runServer(server *http.Server) error {
return server.ListenAndServe()
}
func Close(ctx context.Context, server *http.Server) error {
return server.Shutdown(ctx)
}
Step 3
Create the first endpoint and register it to gin server.
Create a file with the name health in a directory with the name controller in the project folder.
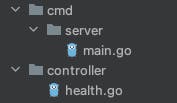
Write the below code in the health.go file
package controller
import (
"net/http"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
func IsHealthy(ctx *gin.Context) {
res := make(map[string]interface{}, 0)
res["status"] = 200
res["healthy"] = "OK"
ctx.JSON(http.StatusOK, res)
}
The last line is where you set the status and the response for the endpoint via gin.Context
Step 4
Register the health endpoint to gin server. Below code snippet shows where and how to register the health endpoint to gin server. Registering can be done in the main.go file.
// remaining code in the code snippet from Step 2
server := &http.Server{
Addr: port,
Handler: engine,
}
engine.GET("/healthcheck", controller.IsHealthy)
chanErrors := make(chan error)
// remaining code in the code snippet from Step 2
Step 5
Now, that there is GET endpoint there are supposed to be tests in place to test the endpoint.
Get assert library which helps in testing the expected value from the actual value.
go get github.com/stretchr/testify
Step 6
Create health_test.go file in the controller directory
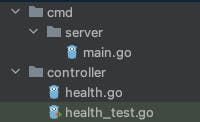
Now add the below code snippet to test the health endpoint. Comments in the code explains what every line does for better understanding.
package controller
import (
"net/http"
"net/http/httptest"
"testing"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"github.com/stretchr/testify/assert"
)
func TestIsHealthy_success(t *testing.T) {
//Create a httptest recorder
responseRecorder := httptest.NewRecorder()
//Create a gin text context for the above recorder to get context and gin engine
ctx, engine := gin.CreateTestContext(responseRecorder)
//Register the healthcheck endpoint to the gin engine
engine.GET("/healthcheck", IsHealthy)
//Create a test request for the above registered endpoint
ctx.Request = httptest.NewRequest(http.MethodGet, "/healthcheck", nil)
//Below line shows how to set headers if necessary
ctx.Request.Header.Set("x-agentname", "agent name")
//Test the endpoint
engine.ServeHTTP(responseRecorder, ctx.Request)
//Assert if response http status is as expected
assert.Equal(t, http.StatusOK, responseRecorder.Code)
}
